The Difference Between Core Cutting and Flat End Milling
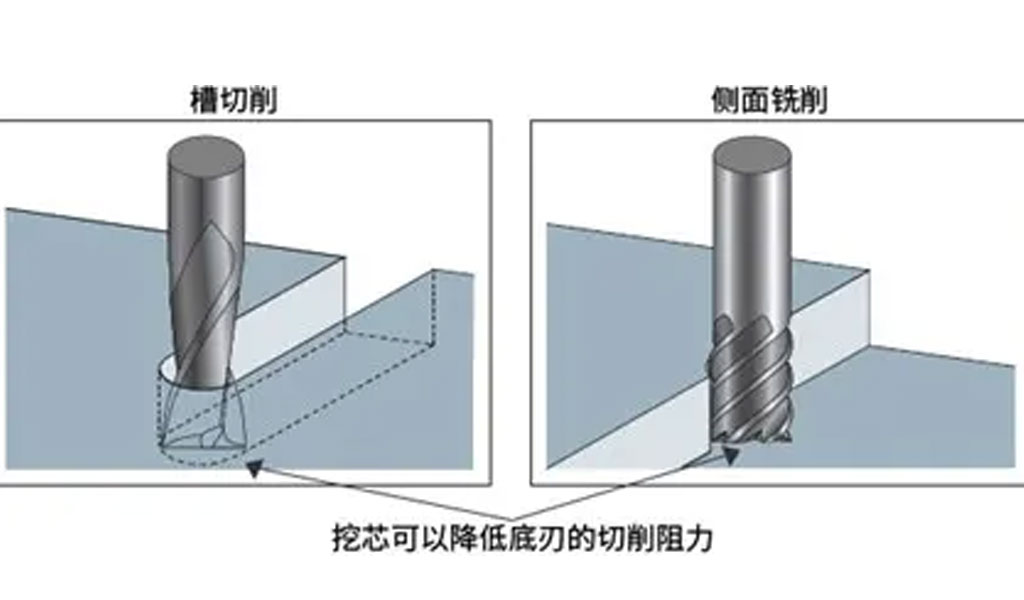
Core cutting and flat end milling are two prominent machining processes utilized in manufacturing industries for material removal and shaping. These techniques are instrumental in producing precise components for a wide range of applications, from aerospace to automotive and beyond. While both involve material removal using rotating cutting tools, they differ significantly in their applications, tool geometries, cutting mechanisms, and results. Understanding these differences is critical for selecting the appropriate method based on project requirements.
Overview of Core Cutting
Core cutting refers to a specialized material removal process often associated with the extraction of a cylindrical or tubular section from a workpiece. This technique is commonly employed when the goal is to create a hollow space or core within the material without compromising the surrounding structure. The term "core" denotes the central part of the material that is removed, typically resulting in a hollow feature or opening.
Core cutting is used extensively in industries requiring high precision and efficiency in creating internal geometries, including construction, engineering, and specialized manufacturing. Applications include making holes in structural steel, producing core samples in geology, and crafting internal features in metal and composite components.
Tools Used in Core Cutting
The tools used for core cutting are designed to maximize material removal efficiency while maintaining the integrity of the surrounding material. Common tools include:
- Core Drills: Cylindrical drills with a hollow center to extract a solid core.
- Hole Saws: Multi-toothed cutting tools ideal for cutting circular holes in metals, plastics, and other materials.
- Diamond Core Bits: Used for cutting hard materials like concrete, ceramics, and stone, especially in construction.
These tools are engineered to reduce cutting forces, minimize heat buildup, and prevent damage to the workpiece.
Overview of Flat End Milling
Flat end milling, a fundamental machining process, involves the removal of material using a rotating tool with a flat cutting edge. Unlike core cutting, which focuses on creating hollow features, flat end milling primarily shapes surfaces, contours, and slots. The process is renowned for its versatility, precision, and ability to produce flat or contoured surfaces.
Flat end milling is a staple in the machining of complex components, making it integral to industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing. The process can handle a wide variety of materials, from soft plastics to hardened steel, by varying the cutting tool and parameters.
Tools Used in Flat End Milling
Flat end milling utilizes cutting tools with a flat tip that provides consistent contact with the workpiece. Key tool types include:
- Flat End Mills: Tools with a square-cutting geometry ideal for producing flat surfaces, grooves, and shoulders.
- Roughing End Mills: Designed with serrated edges for efficient material removal during rough machining.
- High-Speed Steel (HSS) and Carbide End Mills: Available in various coatings for enhanced wear resistance and heat dissipation.
These tools are available in different sizes and configurations to accommodate diverse machining needs.
Key Differences Between Core Cutting and Flat End Milling
1. Objective and Purpose
Core cutting is primarily used for creating hollow structures or extracting material cores, often leaving a cylindrical void or creating a tubular section. In contrast, flat end milling focuses on shaping surfaces, creating slots, and forming complex geometries without extracting a core.
2. Tool Geometry
Core cutting tools, such as core drills and hole saws, feature hollow designs optimized for material extraction. Conversely, flat end mills have solid geometries with sharp edges designed for surface machining and contouring.
3. Material Removal Mechanism
In core cutting, material is removed in the form of a core, minimizing waste and focusing on efficiency. Flat end milling, on the other hand, generates chips as the cutting edge traverses the workpiece.
4. Applications
Core cutting is ideal for creating large-diameter holes, producing cylindrical voids, or extracting material samples. Flat end milling excels in tasks requiring high-precision surface finishes, such as creating mold components, machining flat surfaces, and producing intricate parts.
5. Machining Dynamics
The cutting forces in core cutting are concentrated around the periphery of the tool, reducing the overall load on the cutting edge. Flat end milling distributes forces across the entire cutting edge, which can result in higher tool wear if not managed properly.
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages of Core Cutting
- Material Efficiency: Removes only the core, minimizing material waste.
- Versatility: Effective for hard-to-cut materials like reinforced concrete and metals.
- Precision: Produces clean, precise holes with minimal damage to the surrounding material.
Limitations of Core Cutting
- Tool Wear: Specialized tools like diamond core bits can wear out quickly in abrasive materials.
- Limited Surface Shaping: Focused on creating hollow features rather than detailed contours.
Advantages of Flat End Milling
- Flexibility: Suitable for a wide range of machining tasks, including contouring, slotting, and facing.
- Surface Quality: Produces high-quality surface finishes with the right tool and parameters.
- Tool Availability: Wide range of end mill designs for diverse applications.
Limitations of Flat End Milling
- Material Waste: Generates more waste compared to core cutting.
- Tool Stress: Higher forces on the cutting edge can accelerate tool wear.
Selection Criteria
Choosing between core cutting and flat end milling depends on the following factors:
- Project Requirements: Evaluate whether the task involves hollow feature creation or surface shaping.
- Material Type: Consider the hardness, abrasiveness, and machinability of the material.
- Precision Needs: Determine the level of accuracy and surface finish required.
- Tool Availability: Ensure appropriate tools are available for the specific application.
- Production Volume: High-volume production may favor methods with faster cycle times and lower costs.
Technological Advancements
Recent advancements in machining technology have enhanced the capabilities of both core cutting and flat end milling. Innovations include:
- Tool Coatings: Advanced coatings like TiAlN and diamond coatings improve tool life and performance.
- CNC Integration: Computer numerical control (CNC) systems enable precise control and automation of both processes.
- High-Speed Machining: Increases efficiency and reduces cycle times for milling operations.
- Hybrid Tools: Combination tools that integrate core cutting and milling functionalities.
Applications Across Industries
Core Cutting
- Construction: Creating holes in reinforced concrete for plumbing and electrical conduits.
- Geology: Extracting cylindrical samples for analysis.
- Automotive: Machining tubular components like exhaust systems.
Flat End Milling
- Aerospace: Machining intricate components with high precision.
- Medical: Producing implants and surgical instruments.
- Mold Making: Crafting dies and molds for injection molding.
Reprint Statement: If there are no special instructions, all articles on this site are original. Please indicate the source for reprinting:https://www.cncmachiningptj.com/,thanks!
 PTJ® provides a full range of Custom Precision cnc machining china services.ISO 9001:2015 &AS-9100 certified. 3, 4 and 5-axis rapid precision CNC machining services including milling, turning to customer specifications,Capable of metal & plastic machined parts with +/-0.005 mm tolerance.Secondary services include CNC and conventional grinding, drilling,die casting,sheet metal and stamping.Providing prototypes, full production runs, technical support and full inspection.Serves the automotive, aerospace, mold&fixture,led lighting,medical,bicycle, and consumer electronics industries. On-time delivery.Tell us a little about your project's budget and expected delivery time. We will strategize with you to provide the most cost-effective services to help you reach your target,Welcome to Contact us ( [email protected] ) directly for your new project.
PTJ® provides a full range of Custom Precision cnc machining china services.ISO 9001:2015 &AS-9100 certified. 3, 4 and 5-axis rapid precision CNC machining services including milling, turning to customer specifications,Capable of metal & plastic machined parts with +/-0.005 mm tolerance.Secondary services include CNC and conventional grinding, drilling,die casting,sheet metal and stamping.Providing prototypes, full production runs, technical support and full inspection.Serves the automotive, aerospace, mold&fixture,led lighting,medical,bicycle, and consumer electronics industries. On-time delivery.Tell us a little about your project's budget and expected delivery time. We will strategize with you to provide the most cost-effective services to help you reach your target,Welcome to Contact us ( [email protected] ) directly for your new project.

- 5 Axis Machining
- Cnc Milling
- Cnc Turning
- Machining Industries
- Machining Process
- Surface Treatment
- Metal Machining
- Plastic Machining
- Powder Metallurgy Mold
- Die Casting
- Parts Gallery
- Auto Metal Parts
- Machinery Parts
- LED Heatsink
- Building Parts
- Mobile Parts
- Medical Parts
- Electronic Parts
- Tailored Machining
- Bicycle Parts
- Aluminum Machining
- Titanium Machining
- Stainless Steel Machining
- Copper Machining
- Brass Machining
- Super Alloy Machining
- Peek Machining
- UHMW Machining
- Unilate Machining
- PA6 Machining
- PPS Machining
- Teflon Machining
- Inconel Machining
- Tool Steel Machining
- More Material





