How To Start a CNC Business
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining has become an integral part of modern manufacturing. CNC machines are automated tools that can perform complex and precise tasks in the production of parts and components, ranging from simple designs to highly intricate geometries. The CNC industry serves various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, medical devices, and more. As demand for precision manufacturing grows, starting a CNC business presents a lucrative opportunity for entrepreneurs with the right skills and resources.
This article will provide a comprehensive guide on how to start a CNC business, covering essential aspects such as market research, business planning, legal considerations, equipment acquisition, and marketing strategies.
1. Market Research and Feasibility Study
1.1 Understanding the CNC Industry
Before diving into the CNC business, it is essential to have a clear understanding of the industry. CNC machining involves the use of computer-controlled machines to create precision parts from materials like metals, plastics, and wood. The industry is characterized by high precision, efficiency, and the ability to produce complex parts in large quantities.
1.2 Identifying Target Markets
Determine the specific markets you intend to serve. CNC businesses can cater to a wide range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, medical devices, and more. Understanding the needs of these markets will help you tailor your services and invest in the right equipment.
1.3 Competitor Analysis
Conduct a thorough analysis of existing CNC businesses in your area or target market. Identify their strengths, weaknesses, pricing strategies, and customer base. Understanding your competition will help you position your business more effectively and identify potential gaps in the market.
1.4 Assessing Demand and Profitability
Evaluate the demand for CNC services in your chosen market. Consider factors such as the size of the market, potential customers, and the level of competition. Additionally, assess the profitability of different CNC services and how you can differentiate your offerings to attract clients.
2. Business Planning
2.1 Defining Your Business Model
Determine the scope of your CNC business. Will you offer general CNC machining services, or will you specialize in specific industries or types of machining? Define your service offerings, pricing models, and value proposition.
2.2 Developing a Business Plan
A well-structured business plan is crucial for the success of your CNC business. It should include:
- Executive Summary: An overview of your business, including your mission statement and objectives.
- Market Analysis: Insights from your market research, including target markets, customer segments, and competitor analysis.
- Business Structure: The legal structure of your business (e.g., sole proprietorship, LLC, corporation).
- Service Offerings: Detailed description of the CNC services you will provide.
- Marketing and Sales Strategy: How you plan to attract and retain customers.
- Operational Plan: Day-to-day operations, including production processes, quality control, and supplier management.
- Financial Plan: Budget, funding requirements, revenue projections, and break-even analysis.
2.3 Securing Financing
Starting a CNC business requires significant capital investment in equipment, software, and facilities. Explore various financing options, including personal savings, business loans, investors, and grants. Prepare a compelling financial plan to present to potential lenders or investors.
3. Legal Considerations
3.1 Choosing a Legal Structure
Select the appropriate legal structure for your CNC business. Common options include sole proprietorship, partnership, limited liability company (LLC), and corporation. Each structure has its advantages and disadvantages, affecting taxation, liability, and management.
3.2 Registering Your Business
Register your CNC business with the relevant government authorities. Obtain the necessary licenses and permits to operate legally in your jurisdiction. This may include local business licenses, zoning permits, and environmental permits if applicable.
3.3 Intellectual Property and Patents
If you develop unique processes, products, or software related to CNC machining, consider protecting your intellectual property through patents, trademarks, or copyrights. This can provide a competitive advantage and prevent others from copying your innovations.
3.4 Compliance with Industry Regulations
Ensure that your CNC business complies with industry-specific regulations and standards. This may include quality management standards (e.g., ISO 9001), safety regulations, and environmental standards. Compliance is essential for building trust with customers and avoiding legal issues.
4. Equipment and Technology
4.1 Selecting CNC Machines
The choice of CNC machines is critical to the success of your business. Factors to consider include:
- Type of CNC Machines: Lathes, mills, routers, plasma cutters, and more. Choose machines based on the types of services you plan to offer.
- Machine Specifications: Precision, speed, size, and capabilities. Ensure that the machines meet the requirements of your target market.
- New vs. Used Machines: Decide whether to invest in new machines or purchase used equipment to reduce costs.
4.2 CNC Software and Programming
CNC machines require specialized software for design (CAD) and machine programming (CAM). Invest in reliable software that is compatible with your machines and meets the needs of your clients. Training in CNC programming is essential for efficient and accurate machining.
4.3 Facility Setup
Set up a suitable facility for your CNC operations. Consider factors such as space, ventilation, power supply, and safety measures. The layout of your facility should optimize workflow and ensure the safety of employees.
4.4 Maintenance and Upgrades
Regular maintenance of your CNC machines is crucial to prevent downtime and extend their lifespan. Develop a maintenance schedule and invest in the necessary tools and spare parts. Additionally, plan for future upgrades as technology evolves.
5. Staffing and Training
5.1 Hiring Skilled Workers
Your CNC business will require skilled machinists, programmers, and engineers. Look for candidates with experience in CNC machining, programming, and quality control. Offering competitive salaries and benefits will help you attract top talent.
5.2 Employee Training
Invest in continuous training for your employees to keep them updated on the latest CNC technologies and techniques. Proper training ensures that your staff can operate machines efficiently, reduce errors, and maintain high-quality standards.
5.3 Safety and Compliance Training
CNC machining involves working with heavy machinery and potentially hazardous materials. Implement comprehensive safety training programs to protect your employees and comply with occupational health and safety regulations.
6. Marketing and Sales Strategies
6.1 Branding Your CNC Business
Develop a strong brand identity that reflects the quality and precision of your services. This includes creating a professional logo, website, and marketing materials. Your brand should convey trust, reliability, and expertise.
6.2 Building a Customer Base
Identify potential customers in your target market and develop strategies to reach them. This may include direct marketing, online advertising, attending industry trade shows, and networking with industry professionals. Building relationships with customers is key to securing repeat business.
6.3 Pricing Strategies
Set competitive pricing for your CNC services based on market research, cost analysis, and the value you offer. Consider offering tiered pricing for different levels of service, bulk discounts, and package deals to attract different types of customers.
6.4 Online Presence and Digital Marketing
Establish a strong online presence through a professional website, social media, and digital marketing campaigns. Search engine optimization (SEO), pay-per-click advertising, and content marketing can help you reach a wider audience and generate leads.
6.5 Customer Service and Retention
Providing excellent customer service is essential for retaining clients and generating referrals. Implement a system for tracking customer satisfaction, addressing complaints, and continuously improving your services. Loyal customers are more likely to provide repeat business and recommend your services to others.
7. Financial Management
7.1 Budgeting and Cost Control
Effective financial management is crucial for the sustainability of your CNC business. Develop a detailed budget that covers all aspects of your operations, including equipment, staffing, materials, and overhead costs. Implement cost control measures to maximize profitability.
7.2 Accounting and Bookkeeping
Maintain accurate financial records to track income, expenses, and profitability. Use accounting software to streamline bookkeeping tasks and ensure compliance with tax regulations. Consider hiring an accountant to manage complex financial tasks and provide strategic advice.
7.3 Managing Cash Flow
Cash flow management is critical, especially in the early stages of your business. Monitor cash flow closely to ensure you have sufficient funds to cover operational expenses, payroll, and unexpected costs. Consider using financing options such as lines of credit to manage cash flow during slow periods.
7.4 Profitability and Growth Strategies
Continuously assess the profitability of your CNC business and identify opportunities for growth. This may include expanding your service offerings, entering new markets, or investing in new technology. Developing a long-term growth strategy will help you achieve sustained success.
8. Challenges and Risk Management
8.1 Common Challenges in the CNC Industry
Starting and running a CNC business comes with various challenges, including:
- High Initial Investment: The cost of CNC machines and equipment can be substantial.
- Competition: The CNC industry is competitive, with many established players.
- Technological Changes: Keeping up with rapid advancements in CNC technology can be challenging.
- Supply Chain Issues: Sourcing quality materials and managing suppliers is critical.
8.2 Risk Management Strategies
Implementing risk management strategies can help mitigate potential challenges. This includes:
- Insurance: Protect your business with insurance coverage for property, liability, and equipment.
- Diversification: Diversify your client base and service offerings to reduce reliance on a single market.
- Contingency Planning: Prepare for unexpected events, such as equipment breakdowns or economic downturns.
8.3 Adapting to Industry Trends
Staying informed about industry trends and emerging technologies is essential for maintaining a competitive edge. Attend industry conferences, participate in training programs, and network with other professionals to stay ahead of the curve.
9. Case Studies and Success Stories
9.1 Successful CNC Businesses
Examining the success stories of established CNC businesses can provide valuable insights and inspiration. Case studies can highlight the strategies and practices that have contributed to their growth and success.
9.2 Lessons Learned
Learn from the challenges and mistakes faced by other CNC businesses. Understanding what went wrong and how these businesses overcame obstacles can help you avoid similar pitfalls and make informed decisions.
10. Conclusion
Starting a CNC business requires careful planning, significant investment, and a commitment to quality and precision. By conducting thorough market research, developing a solid business plan, and investing in the right equipment and talent, you can build a successful CNC business that meets the needs of modern manufacturing. As the industry continues to evolve, staying adaptable and focused on customer satisfaction will be key to achieving long-term success.
Reprint Statement: If there are no special instructions, all articles on this site are original. Please indicate the source for reprinting:https://www.cncmachiningptj.com/,thanks!
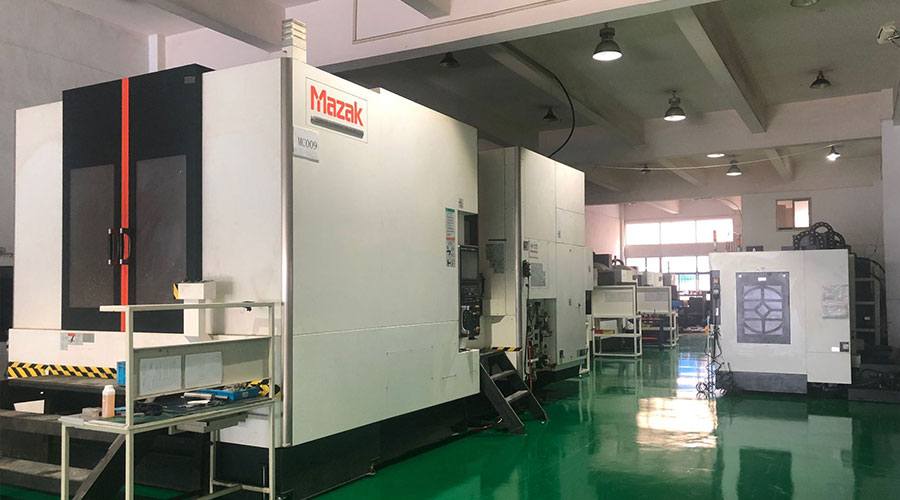 3, 4 and 5-axis precision CNC machining services for aluminum machining, beryllium, carbon steel, magnesium, titanium machining, Inconel, platinum, superalloy, acetal, polycarbonate, fiberglass, graphite and wood. Capable of machining parts up to 98 in. turning dia. and +/-0.001 in. straightness tolerance. Processes include milling, turning, drilling, boring, threading, tapping, forming, knurling, counterboring, countersinking, reaming and laser cutting. Secondary services such as assembly, centerless grinding, heat treating, plating and welding. Prototype and low to high volume production offered with maximum 50,000 units. Suitable for fluid power, pneumatics, hydraulics and valve applications. Serves the aerospace, aircraft, military, medical and defense industries.PTJ will strategize with you to provide the most cost-effective services to help you reach your target,Welcome to Contact us ( [email protected] ) directly for your new project.
3, 4 and 5-axis precision CNC machining services for aluminum machining, beryllium, carbon steel, magnesium, titanium machining, Inconel, platinum, superalloy, acetal, polycarbonate, fiberglass, graphite and wood. Capable of machining parts up to 98 in. turning dia. and +/-0.001 in. straightness tolerance. Processes include milling, turning, drilling, boring, threading, tapping, forming, knurling, counterboring, countersinking, reaming and laser cutting. Secondary services such as assembly, centerless grinding, heat treating, plating and welding. Prototype and low to high volume production offered with maximum 50,000 units. Suitable for fluid power, pneumatics, hydraulics and valve applications. Serves the aerospace, aircraft, military, medical and defense industries.PTJ will strategize with you to provide the most cost-effective services to help you reach your target,Welcome to Contact us ( [email protected] ) directly for your new project.

- 5 Axis Machining
- Cnc Milling
- Cnc Turning
- Machining Industries
- Machining Process
- Surface Treatment
- Metal Machining
- Plastic Machining
- Powder Metallurgy Mold
- Die Casting
- Parts Gallery
- Auto Metal Parts
- Machinery Parts
- LED Heatsink
- Building Parts
- Mobile Parts
- Medical Parts
- Electronic Parts
- Tailored Machining
- Bicycle Parts
- Aluminum Machining
- Titanium Machining
- Stainless Steel Machining
- Copper Machining
- Brass Machining
- Super Alloy Machining
- Peek Machining
- UHMW Machining
- Unilate Machining
- PA6 Machining
- PPS Machining
- Teflon Machining
- Inconel Machining
- Tool Steel Machining
- More Material





